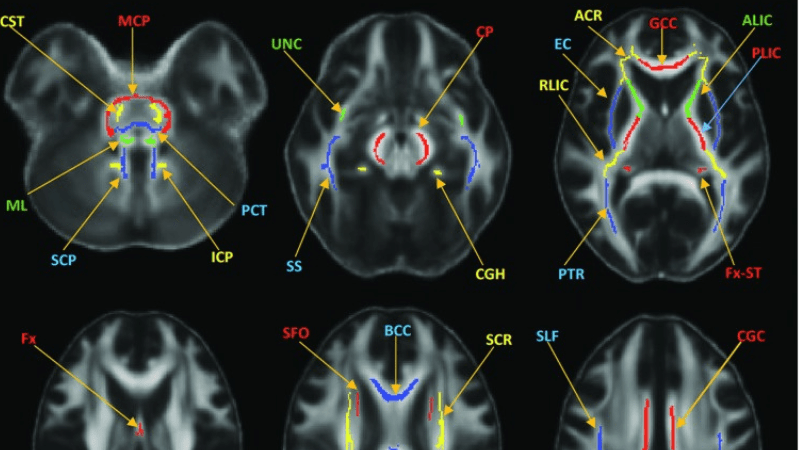
The Wu lab addresses the sensitivity issues of conventional medical imaging techniques in detecting mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) by utilizing hybrid diffusion imaging (HYDI). By employing advanced diffusion imaging techniques such as neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging (NODDI) and q-space analyses, the study identified significant white matter alterations in patients with mTBI compared to trauma control patients. Furthermore, correlations between diffusion metrics and neuropsychological test results revealed potential biomarkers for mTBI, indicating that NODDI-derived axonal density index and q-space measures could serve as sensitive indicators of white matter changes associated with mTBI.