The research laboratory of Mark R. Kelley, MS, PhD focuses on translational research in DNA damage and repair, specifically, to determine how those activities can be exploited therapeutically to treat cancers and protect normal cells from oxidative and DNA base damage. We have focused specifically on the enzyme apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1/ Redox effector factor-1 (APE1/Ref-1)—mechanistically as well as a therapeutic target in cancers and other diseases that manifest cancer-like properties. APE1/Ref-1 is unique to the Base Excision Repair Pathway (BER), with dual repair and redox signaling functions that are crucial to cellular viability. We have concentrated on teasing apart these functions and in the process, we have discovered and have been developing redox-specific inhibitors of Ref-1.This original work was the impetus for becoming Chief Scientific Founder and Officer of Apexian Pharmaceutical targeting Ref-1 to produce new therapeutics for some of the deadliest and hardest-to-treat cancers. Apexian recently completed a phase I clinical trial using oral APX3330 in solid tumor patients (NCT03375086). Phase II trials are being developed in cancer and other indications including ocular diseases. A phase IIb trial using APX3330 in diabetic retinopathy (DR) has recently completed (NCT04692688) using a drug we developed and licensed to Ocuphire Pharma. Our lab is dedicated to fast-tracking collaboration and translational research to find more effective cancer treatments as well as treatments for other diseases related to APE1/Ref-1. All of the discoveries during my career have culminated in 19 patents and over 196 articles in peer reviewed journals as well as 36 review articles/book chapters, attesting to my contributions to the field of DNA repair, redox signaling and drug development. I am a recent AAAS Science Fellow (2022). Current h index is 76.
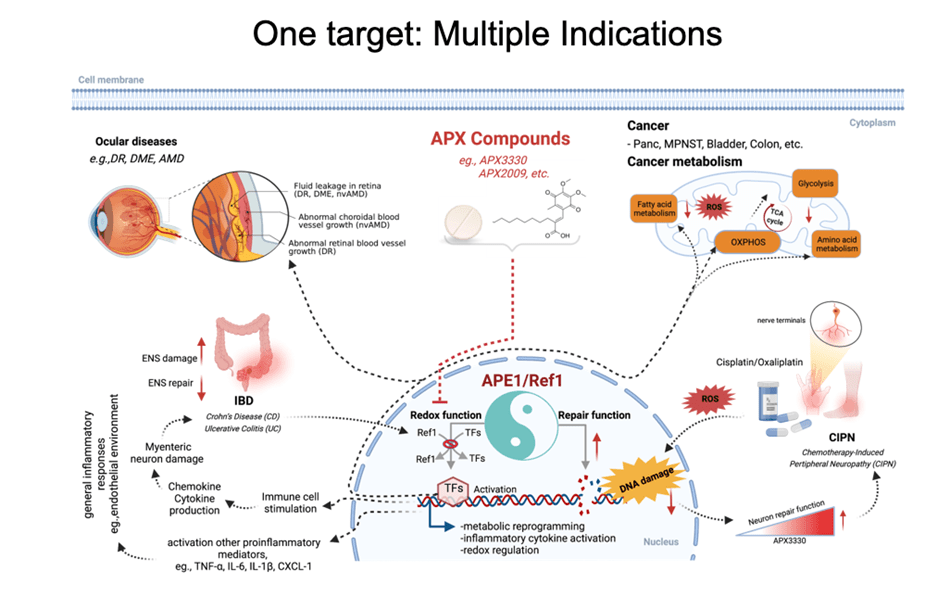
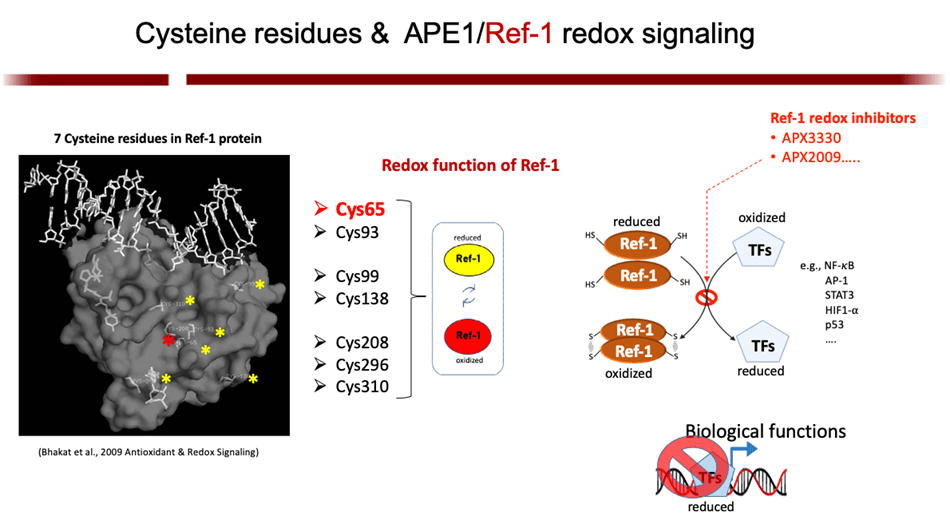
The Base Excision Repair (BER) pathway is the body’s main defense in repairing oxidative damage to DNA. The most singular BER protein that has no “backup” or equivalent is APE1/Ref-1. Its dual name alludes to its unique dual functions as an AP endonuclease and as a redox effector factor (the “Ref” part of its name). Since 1987, I have studied BER extensively and was the first to fully characterize APE1/Ref-1’s translational and clinical relevance and differentiate its functions using chemical molecules (findings published in 1995, 2001, and more recently). While the fully folded protein performs its endonuclease function a locally unfolded configuration of the protein performs redox activities at its amino terminus. Unlike other redox proteins, APE1/Ref-1’s cysteine residues are buried. Also, unlike other redox proteins that require two cysteine residues, APE1/Ref-1 requires three to perform its complex redox functions (published in 2012 and 2013). My efforts in these areas have given me an unprecedented advantage in developing a new class of therapeutics that can selectively modify one function or the other.
- Su, D., Delaplane, S., Luo, M., Rempel, D., Vu, B., Kelley, M. R., Gross, M. L., & Georgiadis, M. (2011). Interactions of APE1with a redox inhibitor: Evidence for an alternate conformation of the enzyme. Biochemistry, 50(1), 82-92. PMCID: PMC3070192
- Luo, M., Zhang, J., He. H., Su, D., Chen, Q., Gross, M., Kelley, M. R., & Georgiadis, M. (2012). Characterization of the Redox Activity and Disulfide Bond Formation in Apurinic / Apyrimidinic Endonuclease. Biochemistry, 51(2), 695-705. PMCID: PMC3293223
- Zhang, J., Luo, M., Marascot, D., Logsdon, D., LaFavers, K. A., Chen, Q., Reed, A., Kelley, M. R., Gross, M. L., & Georgiadis, M. M. (2013). Inhibition of Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease I’s redox activity revisited. Biochemistry, 52(17), 2955-66. PMCID: PMC3706204
- M.R. Kelley, J.H. Wikel, C. Guo, K.E. Pollok, B.J. Bailey, R. Wireman, M.L. Fishel, and M.R. Vasko. (2016) Identification and Characterization of new chemical entities targeting apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 for the prevention of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2016 Nov;359(2):300-309. Epub 2016 Sept 8. DOI:10.1124/jpet.116.235283. PMCID: PMC5074487
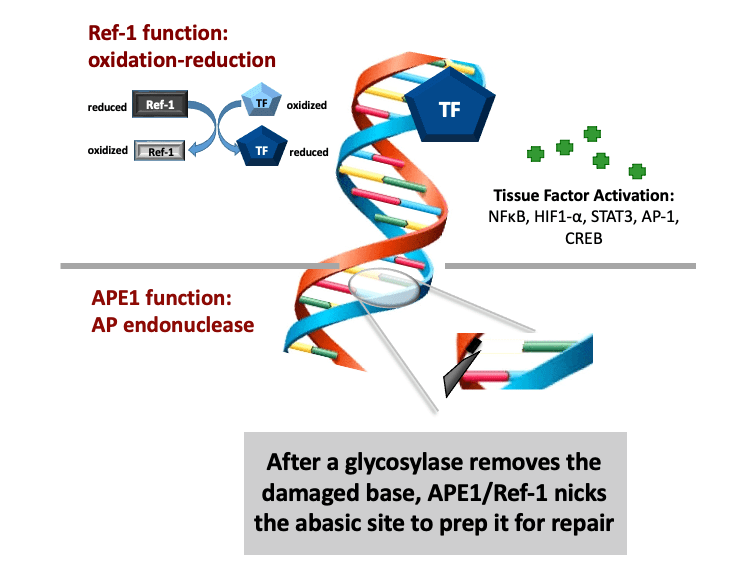
APE1/Ref-1 is a master regulator of oxidative stress; and, as such, its redox activity maintains many transcription factors by keeping them in their active (reduced) state. Many of those factors are involved in cell growth, progression, proliferation, apoptosis, angiogenesis, and inflammation. I have shown that upregulation of APE1 occurs in many solid cancers (pancreatic, colon, bladder, etc) and sarcomas (e.g. MPNST), contributing to therapeutic resistance. This is especially true with pancreatic cancer (PDAC). Inhibition of APE1’s redox activity blocks their proliferation and migration by decreasing the transcription activity of NF-κB, AP-1, HIF-1α and STAT3—key factors involved survival, invasion, and metastasis.
- F. Shah, E. Goossens, N.M. Atallah, M. Grimard. M.R. Kelley, and M.L Fishel. (2017) Characterizing gene expression changes and identifying novel pathways following APE1/Ref-1 knockdown in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma using Single-cell RNA Sequencing. Mol Oncol. 2017 Dec;11(12):1711-1732. PMCID: PMC5709621
- Gampala S, Shah F, Zhang C, Rhodes SD, Babb O, Grimard M, Wireman RS, Rad E, Calver B, Bai RY, Staedtke V, Hulsey EL, Saadatzadeh MR, Pollok KE, Tong Y, Smith AE, Clapp DW, Tee AR, Kelley MR, Fishel ML. (2021) Exploring transcriptional regulators Ref-1 and STAT3 as therapeutic targets in malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors. Br J Cancer. Apr;124(9):1566-1580. doi: 10.1038/s41416-021-01270-8. Epub 2021 Mar 3. PMID: 33658640; PMCID: PMC8076291.
- Caston RA, Shah F, Starcher CL, Wireman R, Babb O, Grimard M, McGeown J, Armstrong L, Tong Y, Pili R, Rupert J, Zimmers TA, Elmi AN, Pollok KE, Motea EA, Kelley MR, Fishel ML. (2021) Combined inhibition of Ref-1 and STAT3 leads to synergistic tumor inhibition in multiple cancers using 3D and in vivo tumour co-culture models. J Cell Mol Med. Jan;25(2):784-800. PMID: 33274592; PMCID: PMC7812272.
- Mijit M, Wireman R, Armstrong L, Gampala S, Hassan Z, Schneeweis C, Schneider G, Zhang C, Fishel ML and Kelley MR (2022) RelA Is an Essential Target for Enhancing Cellular Responses to the DNA Repair/Ref-1 Redox Signaling Protein and Restoring Perturbated Cellular Redox Homeostasis in Mouse PDAC Cells. Front. Oncol. 12:826617. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.826617
- Luo, M., Delaplane, S., Jiang, A., Reed, A., He, Y., Fishel, M., Nyland II, R., Borch, R. F., Qiao, X., Georgiadis, M. M., & Kelley, M. R. (2008). Role of the multifunctional DNA repair and redox signaling protein Ape1/Ref-1 in cancer and endothelial cells: Small molecule inhibition of Ape1’s redox function. Antiox Redox Signal, 10(11), 1853-1867. PMCID: PMC2587278
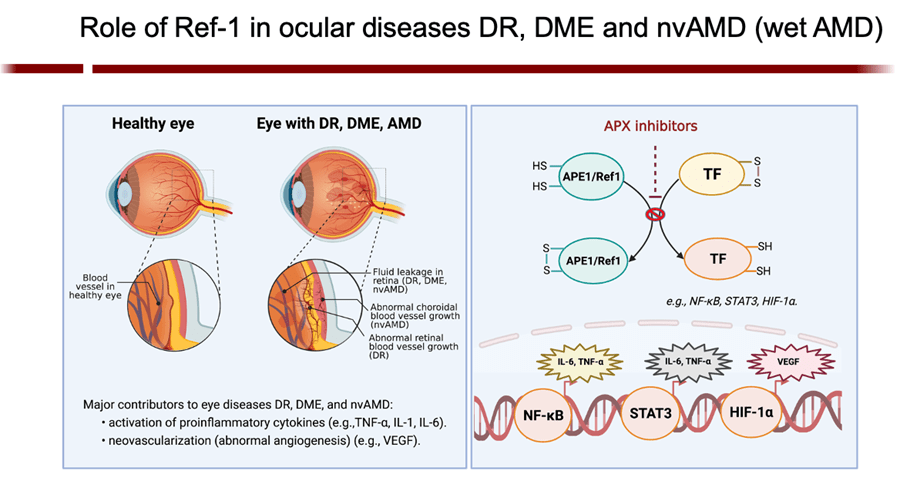
- Jiang, A., Gao, H., Kelley, M. R., & Qiao, X. (2011). Inhibition of APE1/Ref-1 Redox Activity with APX3330 Blocks Retinal Angiogenesis In Vitro and In Vivo. Vision Res, 51, 93-100. PMCID: PMC3010438
- J.C. Fehrenbacher, C. Guo, M.R. Kelley, and M.R. Vasko. (2017) DNA damage mediates changes in neuronal sensitivity induced by the inflammatory mediators, MCP-1 and LPS, and can be reversed by enhancing the DNA repair function of APE1. Neuroscience. 2017 Dec 16:366:23-25. PMID: 28965839
- Pasha S, Sishtla K, Sulaiman RS, Park B, Shetty T, Shah F, Fishel ML, Wikel JH, Kelley MR, Corson TW. (2018) Ref-1/APE1 Inhibition with Novel Small Molecules Blocks Ocular Neovascularization. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. Oct;367(1):108-118. PMID:30076264
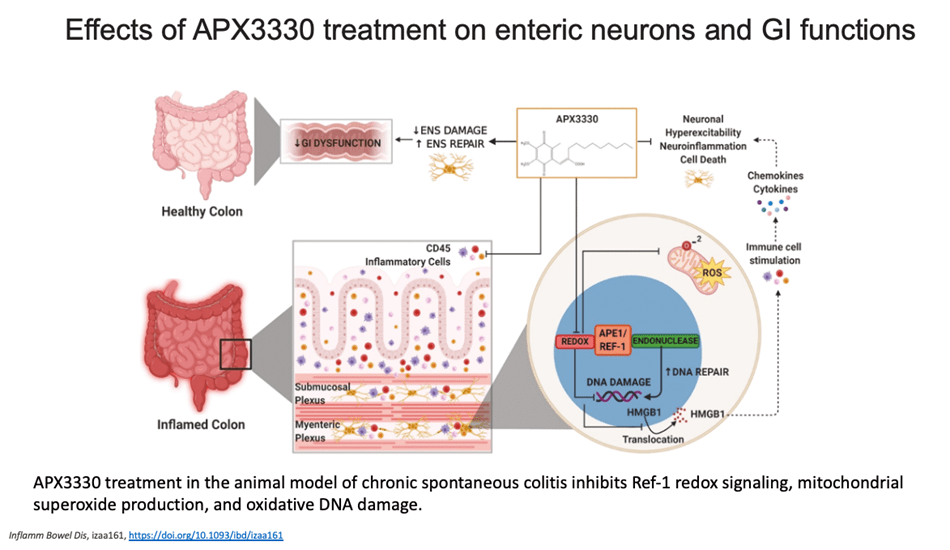
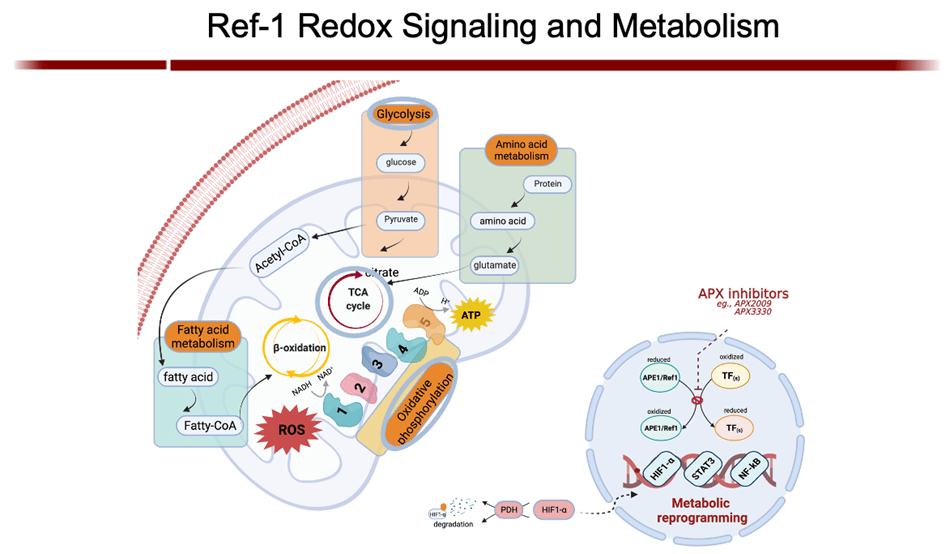
My group is the first to develop an inhibitor of APE1 of its redox signaling function for clinic. APX3330, has completed phase I clinical trials for safety and RP2D in cancer patients (NCT03375086). We have also discovered that APX3330 and 2nd generation compounds have anti-CIPN properties along with anti-tumor. This has potential win-win for patients; anti-cancer and anti-CIPN. APE1 redox inhibition also holds promise as a potential treatment for inflammatory-based diseases, as well as situations where anti-angiogenic agents are used alone and to enhance the effectiveness of those agents such as DR/DME, wet age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn’s and colitis). Apexian recently completed a phase I clinical trial using oral APX3330 in solid tumor patients (NCT03375086). This trial established safety, expected PK, target engagement, and responses in patients in the trial. Phase II trials are being developed in cancer and other indications including ocular diseases. A phase II trial using APX3330 in diabetic retinopathy (DR) and diabetic macular edema (DME) recently began accruing patients (NCT04692688).
- Cai Z, Kotzin JJ, Ramdas B, Chen S, Nelanuthala S, Palam LR, Pandey R, Mali RS, Liu Y, Kelley MR, Sandusky G, Mohseni M, Williams A, Henao-Mejia J, Kapur R. (2018) Inhibition of Inflammatory Signaling in Tet2 Mutant Preleukemic Cells Mitigates Stress-Induced Abnormalities and Clonal Hematopoiesis.Cell Stem Cell. 2018 Dec 6;23(6):833-849. PMID:30526882
- S. Pasha, K. Sishtla, R.S. Sulaiman, B. Park, T. Shetty, F. Shah, M.L. Fishel, J.H. Wikel, M.R. Kelley, and T.W. Corson. (2018) Ref-1/APE1 inhibition with novel small molecules blocks ocular neovascularization. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 367:108-118. PMID: 30076264
- Gampala S, Shah F, Zhang C, Rhodes SD, Babb O, Grimard M, Wireman RS, Rad E, Calver B, Bai RY, Staedtke V, Hulsey EL, Saadatzadeh MR, Pollok KE, Tong Y, Smith AE, Clapp DW, Tee AR, Kelley MR, Fishel ML. (2021) Exploring transcriptional regulators Ref-1 and STAT3 as therapeutic targets in malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors. Br J Cancer. Apr;124(9):1566-1580. PMID: 33658640.
- Sahakian L, Filippone R, Stavely R, Robinson A, Yan X, Abalo R, Eri R, Bornstein J, Kelley MR, Nurgali K. (2021) Inhibition of APE1/Ref-1 redox signaling alleviates intestinal dysfunction and enteric nervous system damage in a mouse model of chronic colitis, Inflam. Bowel Dis. Feb 16;27(3):388-406. PMID: 32618996
Research Funding
Exploiting the Ref-1 node in pancreatic cancer: tailoring new pancreatic cancer therapy using multi-targeted combinations
Goals: Study the role and interaction of Ref-1 in tumor and stroma of PDAC as well as identifying potential new combination targets affecting the Ref-1 signaling node.
Targeting the Ref-1 signaling node for treating ocular neovascularization
Goal: To dissect the mechanisms of Ref-1 as a mediator of angiogenesis and inflammation in the eye.
(PQ12) Enhancement of DNA repair in neurons via a targeted APE1 small molecule modifier to decrease and reverse chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) using a first-in-class modifier
Goals: To apply the knowledge gained from understanding that DNA damage is critical for the development of neuropathy and advancing the development of a new treatment strategy by pharmacologically modifying APE1-mediated DNA repair.
(PQ9) Mechanistic Role of APE1 and BER in chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy
Goals: Determine the mechanistic role of APE1 and BER following platinum therapies and induction or protection from CIPN.
Hyperglycemia mediated myeloproliferative disease
Goals: Role of inflammation and diabetes in induction of myeloproliferative disease
American Cancer Society
IU Simon Comprehensive Cancer Center Institutional Research Grant
Goals: Institutional ACS grant to furnish young investigators with pilot funding
Cancer Center Support Grant
Goals: Associate Director of Basic Science responsibilities and roles
Role: Associate Director of Basic Science
Testing Apexian compounds for efficacy in cancer models and biomarker discovery
Goals: Testing new Ref-1 redox inhibitors in leukemia models for efficacy
Big Data Training for Cancer Research
Goals: Informatics training course for cancer researchers in big data and bioinformatics
Role: Co-Investigator
Recent Publications
Sahakian L, Filippone R, Stavely R, Robinson A, Yan X, Abalo R, Eri R, Bornstein J, Kelley MR, Nurgali K. (2021) Inhibition of APE1/Ref-1 redox signalling alleviates intestinal dysfunction and enteric nervous system damage in a mouse model of chronic colitis, Inflammatory Bowel Disease Feb 16;27(3):388-406. PMID: 32618996
Gampala S, Shah F, Zhang C, Rhodes SD, Babb O, Grimard M, Wireman RS, Rad E, Calver B, Bai RY, Staedtke V, Hulsey EL, Saadatzadeh MR, Pollok KE, Tong Y, Smith AE, Clapp DW, Tee AR, Kelley MR, Fishel ML. (2021) Exploring transcriptional regulators Ref-1 and STAT3 as therapeutic targets in malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors. Br J Cancer. Apr;124(9):1566-1580. doi: 10.1038/s41416-021-01270-8. Epub 2021 Mar 3. PMID: 33658640; PMCID: PMC8076291.
Caston RA, Shah F, Starcher CL, Wireman R, Babb O, Grimard M, McGeown J, Armstrong L, Tong Y, Pili R, Rupert J, Zimmers TA, Elmi AN, Pollok KE, Motea EA, Kelley MR, Fishel ML. (2021) Combined inhibition of Ref-1 and STAT3 leads to synergistic tumor inhibition in multiple cancers using 3D and in vivo tumour co-culture models. J Cell Mol Med. Jan;25(2):784-800. PMID: 33274592; PMCID: PMC7812272.
Gampala S, Shah F, Lu X, Moon HR, Babb O, Umesh Ganesh N, Sandusky G, Hulsey E, Armstrong L, Mosely AL, Han B, Ivan M, Yeh JJ, Kelley MR, Zhang C, Fishel ML. (2021) Ref-1 redox activity alters cancer cell metabolism in pancreatic cancer: Exploiting this novel finding as a potential target. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Aug 10;40(1):251. PMID: 34376225
Mijit M, Wireman R, Armstrong L, Gampala S, Hassan Z, Schneeweis C, Schneider G, Zhang C, Fishel ML and Kelley MR (2022) RelA Is an Essential Target for Enhancing Cellular Responses to the DNA Repair/Ref-1 Redox Signaling Protein and Restoring Perturbated Cellular Redox Homeostasis in Mouse PDAC Cells. Front. Oncol. 12:826617. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.826617
Research Team
Eyram Kpenu, Medical/Graduate Student
Randy Wireman, Research Analyst
Dr. Sanya Haiary, Postdoctoral Fellow
